前言
MyBatis是一个流行的ORM框架,它简单易用,支持自定义SQL、存储过程以及高级映射。MyBatis免除了几乎所有的JDBC代码以及设置参数和获取结果集的工作。
作为一款优秀的持久层框架,连接池是必不可少的。本文将分析MyBatis内置的数据源是如何实现连接池功能的(源码基于MyBatis3.4.5)。
JDBC对数据库的操作
回忆一下,我们用原生的JDBC来操作数据库的一般流程:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
public class JDBCExample {
// JDBC driver name and database URL / credentials
static final String JDBC_DRIVER = "com.mysql.jdbc.Driver";
static final String DB_URL = "jdbc:mysql://localhost/EMP";
static final String USER = "username";
static final String PASS = "password";
public List<User> queryUsers() {
Connection conn = null;
Statement stmt = null;
ResultSet rs = null;
List<User> users = new ArrayList<>();
try {
// STEP 1: 注册driver
Class.forName(JDBC_DRIVER);
// STEP 2: 打开连接
conn = DriverManager.getConnection(DB_URL,USER,PASS);
// STEP 3: 执行query
stmt = conn.createStatement();
String sql = "SELECT ID, NAME, AGE FROM USER";
rs = stmt.executeQuery(sql);
// STEP 4: 获取变量
while(rs.next()) {
User user = new User();
user.setId(rs.getInt("ID"));
user.setAge(rs.getInt("AGE"));
user.setName(rs.getString("NAME"));
users.add(user);
}
return users;
} catch(SQLException | ClassNotFoundException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} finally {
// STEP 5: 关闭资源
try {
if (rs != null)
rs.close();
if (stmt != null)
stmt.close();
if (conn != null)
conn.close();
} catch(SQLException se) {
se.printStackTrace();
}
}
return users;
}
}
主要的步骤包括:
- 加载数据库驱动
- 获取数据库连接
- 执行
SQL语句 - 从
ResultSet获取结果,给Entity赋值 - 关闭数据库连接等资源
不难发现,当中包含了大段的重复模版代码。而我们所关心的业务逻辑,只有寥寥几行。而且,每执行一次数据库操作都重新建立一个新的连接,用完之后关闭的做法,性能非常低。因为每次打开关闭连接,都会涉及到TCP的三次握手与四次挥手,以及数据库的验证操作。为了优化第二个问题,出现了数据库连接池。
数据库连接池
不管是Connection Pool,Thread Pool还是Channel Pool,所有池的思想都是一致的:
- 维护一个资源集合
- 消费者可以从集合中获取资源
- 消费者使用完资源后,将之放回池中
当然其中肯定会涉及到一些池的大小的维护,池满之后的处理等细节操作。接下来我们来分析一下MyBatis中的连接池是如何实现的。
MyBatis中的连接池实现
如果我们使用MyBatis内置的数据源的化,一般会在XML配置文件里面这样配置:
1
2
3
4
5
6
<dataSource type="POOLED">
<property name="driver" value="${driver}"/>
<property name="url" value="${url}"/>
<property name="username" value="${username}"/>
<property name="password" value="${password}"/>
</dataSource>
其中dataSource的type配置为POOLED,则MyBatis会使用org.apache.ibatis.datasource.pooled.PooledDataSource作为数据源。下面是PooledDataSource的类变量:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
// PooledDataSource
public class PooledDataSource implements DataSource {
// 用来维护连接池的状态
private final PoolState state = new PoolState(this);
// 这里用了组合模式,像driver,url,username,password
// 之类的配置变量信息存在UnpooledDataSource中
private final UnpooledDataSource dataSource;
// 连接池的信息,可定制化配置
protected int poolMaximumActiveConnections = 10;
protected int poolMaximumIdleConnections = 5;
protected int poolMaximumCheckoutTime = 20000;
protected int poolTimeToWait = 20000;
protected String poolPingQuery = "NO PING QUERY SET";
protected boolean poolPingEnabled = false;
protected int poolPingConnectionsNotUsedFor = 0;
private int expectedConnectionTypeCode;
}
注意,PooledDataSource将一部分配置信息放在了UnpooledDataSource中,并用了一个PoolState来维护连接池的状态:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
// UnpooledDataSource
// PooledDataSource可以看成是由UnpooledDataSource扩展而来的,所以复用了一些变量
public class UnpooledDataSource implements DataSource {
// 包含了如username,password的】等配置信息
private ClassLoader driverClassLoader;
private Properties driverProperties;
private boolean driverInitialized;
private String driver;
private String url;
private String username;
private String password;
private boolean autoCommit;
private Integer defaultTransactionIsolationLevel;
}
// PoolState
public class PoolState {
protected PooledDataSource dataSource;
// 空闲连接列表
protected final List<PooledConnection> idleConnections = new ArrayList<PooledConnection>();
// 活跃连接列表
protected final List<PooledConnection> activeConnections = new ArrayList<PooledConnection>();
// 从连接池中获取连接的次数
protected long requestCount = 0;
// 请求连接总耗时(ms)
protected long accumulatedRequestTime = 0;
// 连接执行时间总耗时
protected long accumulatedCheckoutTime = 0;
// 执行时间超时的连接数
protected long claimedOverdueConnectionCount = 0;
// 总共超时时间
protected long accumulatedCheckoutTimeOfOverdueConnections = 0;
// 总共等待时间
protected long accumulatedWaitTime = 0;
// 等待次数
protected long hadToWaitCount = 0;
// 无效连接数
protected long badConnectionCount = 0;
}
获取连接
好了,对类的成员变量有了一个直观的概念之后,我们分析来看连接池是如何实现的。找到获取连接的主方法popConnection():
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
83
84
85
86
87
88
89
90
91
92
93
94
95
96
97
98
// PooledDataSource
private PooledConnection popConnection(String username, String password) throws SQLException {
boolean countedWait = false;
PooledConnection conn = null;
long t = System.currentTimeMillis();
int localBadConnectionCount = 0;
// 需要不断尝试获取连接,所以放在循环里
while (conn == null) {
// 为线程安全,加synchronized锁
synchronized (state) {
// 检查空间连接列表是不是为空
if (!state.idleConnections.isEmpty()) {
// 如果有空闲连接可用,那么直接获取列表第一个连接并将之从列表中删除
conn = state.idleConnections.remove(0);
} else {
// 无空闲连接可用时,走到这里
if (state.activeConnections.size() < poolMaximumActiveConnections) {
// 如果活跃连接数未超出限制,则新建连接
// dataSource.getConnection()的逻辑是初始化driver,从DriverManager获取连接,
// 设置autoCommit和IsolationLevel,比较简单,就不分析了
conn = new PooledConnection(dataSource.getConnection(), this);
} else {
// 连接池已满,取出运行时间最长的连接
// 列表中的连接是按照运行时间排序的,所以第一个元素就是运行时间最长的
PooledConnection oldestActiveConnection = state.activeConnections.get(0);
long longestCheckoutTime = oldestActiveConnection.getCheckoutTime();
// 如果运行时间超过超时时间
if (longestCheckoutTime > poolMaximumCheckoutTime) {
// 更新一些统计字段
state.claimedOverdueConnectionCount++;
state.accumulatedCheckoutTimeOfOverdueConnections += longestCheckoutTime;
state.accumulatedCheckoutTime += longestCheckoutTime;
// 将超时连接移出 活跃连接列表
state.activeConnections.remove(oldestActiveConnection);
// 如果未设置自动提交,则进行回滚操作
if (!oldestActiveConnection.getRealConnection().getAutoCommit()) {
oldestActiveConnection.getRealConnection().rollback();
}
// 创建一个新的连接,不过需要复用oldestActiveConnection的realConnection,
// 实际上并没有创建新的数据库连接
conn = new PooledConnection(oldestActiveConnection.getRealConnection(), this);
// 复用oldestActiveConnection 的一些信息,将oldestActiveConnection设置为无效
conn.setCreatedTimestamp(oldestActiveConnection.getCreatedTimestamp());
conn.setLastUsedTimestamp(oldestActiveConnection.getLastUsedTimestamp());
oldestActiveConnection.invalidate();
} else {
// 未超时
try {
// 记录统计信息
if (!countedWait) {
state.hadToWaitCount++;
countedWait = true;
}
long wt = System.currentTimeMillis();
// 调用Object.wait()方法进入等待状态
state.wait(poolTimeToWait);
// 记录统计信息
state.accumulatedWaitTime += System.currentTimeMillis() - wt;
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
break;
}
}
}
}
if (conn != null) {
// 检测连接是否有效,主要会检测PooledConnection.valid字段,
// 以及执行SQL ping的语句查看数据库状态,这里不做分析
if (conn.isValid()) {
// 如果没有设置自动回滚,执行回滚操作
if (!conn.getRealConnection().getAutoCommit()) {
conn.getRealConnection().rollback();
}
// 更新一些统计字段
conn.setConnectionTypeCode(assembleConnectionTypeCode(dataSource.getUrl(), username, password));
conn.setCheckoutTimestamp(System.currentTimeMillis());
conn.setLastUsedTimestamp(System.currentTimeMillis());
state.activeConnections.add(conn);
state.requestCount++;
state.accumulatedRequestTime += System.currentTimeMillis() - t;
} else {
// 更新无效连接相关的统计字段
state.badConnectionCount++;
localBadConnectionCount++;
conn = null;
if (localBadConnectionCount > (poolMaximumIdleConnections + 3)) {
throw new SQLException("PooledDataSource: Could not get a good connection to the database.");
}
}
}
}
}
// 如果没有获取到连接,直接抛出异常
if (conn == null) {
throw new SQLException("PooledDataSource: Unknown severe error condition. The connection pool returned a null connection.");
}
return conn;
}
以上就是获取连接的主要逻辑,大致如下:
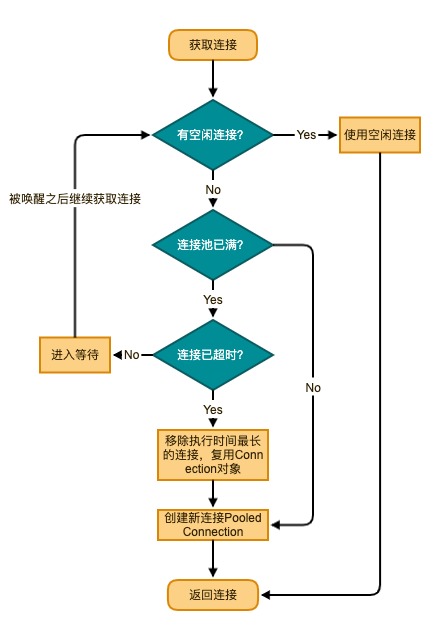
这里有个疑问,我们外部获取连接用的都是getConnection()方法,而不是popConnection()方法。那么让我们来看看getConnection()是如何实现的:
1
2
3
public Connection getConnection() throws SQLException {
return popConnection(dataSource.getUsername(), dataSource.getPassword()).getProxyConnection();
}
除了调用popConnection()方法之外,还调用了getProxyConnection(),看名字是包装了一层代理。为什么要这样做呢?这就需要看释放连接的逻辑了。
释放连接
MyBatis用代理模式(如果对此模式不了解的,推荐看一下这篇文章),将数据库连接包装在PooledConnection对象之中:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
// PooledConnection
class PooledConnection implements InvocationHandler {
// 关闭连接的方法close(),在代理中拦截此方法来做释放连接的操作
private static final String CLOSE = "close";
private static final Class<?>[] IFACES = new Class<?>[] { Connection.class };
private final int hashCode;
// 数据源对象,这里即PooledDataSource
private final PooledDataSource dataSource;
// 真正的从DriverManager中获取出来的连接
private final Connection realConnection;
// realConnection的代理对象
private final Connection proxyConnection;
// 一些参数
private long checkoutTimestamp;
private long createdTimestamp;
private long lastUsedTimestamp;
private int connectionTypeCode;
private boolean valid;
// 构造方法
public PooledConnection(Connection connection, PooledDataSource dataSource) {
this.hashCode = connection.hashCode();
this.realConnection = connection;
this.dataSource = dataSource;
this.createdTimestamp = System.currentTimeMillis();
this.lastUsedTimestamp = System.currentTimeMillis();
this.valid = true;
// proxyConnection使用了JDK的动态代理,并将自己(this)作为了InvocationHandler
this.proxyConnection = (Connection) Proxy.newProxyInstance(Connection.class.getClassLoader(), IFACES, this);
}
public Connection getProxyConnection() {
return proxyConnection;
}
}
注意最后的getProxyConnection()方法,发现它果然返回了一个Connection的代理对象。同时,由于PooledConnection实现了InvocationHandler接口,当外部调用代理对象方法时,都会转为调用InvocationHandler.invoke()方法。于是下面主要看invoke()方法是如何实现的:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
// PooledConnection
public Object invoke(Object proxy, Method method, Object[] args) throws Throwable {
String methodName = method.getName();
// 如果调用了close()方法,即调用方需要关闭连接
if (CLOSE.hashCode() == methodName.hashCode() && CLOSE.equals(methodName)) {
// 转为调用pushConnection()方法
dataSource.pushConnection(this);
return null;
} else {
try {
// 如果不是调用的close()方法,则调用realConnection的同名方法
return method.invoke(realConnection, args);
} catch (Throwable t) {
throw ExceptionUtil.unwrapThrowable(t);
}
}
}
看到这里,出现了闭环。调用方使用完连接之后,如果调用了close()方法,会被上述方法拦截,转为调用dataSource.pushConnection(this)方法,猜测这个方法是用来将连接放回连接池中的。我们来一探究竟:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
// PooledDataSource
protected void pushConnection(PooledConnection conn) throws SQLException {
// 与popConnection方法一样,同样也在state上加锁,用来做线程间协作
synchronized (state) {
// 从活跃连接中移除此连接
state.activeConnections.remove(conn);
if (conn.isValid()) {
// 空闲连接未满
if (state.idleConnections.size() < poolMaximumIdleConnections && conn.getConnectionTypeCode() == expectedConnectionTypeCode) {
state.accumulatedCheckoutTime += conn.getCheckoutTime();
// 若未设置autoCommit,执行回滚
if (!conn.getRealConnection().getAutoCommit()) {
conn.getRealConnection().rollback();
}
// 创建新的PooledConnection,并加入到idleConnections列表的末尾
PooledConnection newConn = new PooledConnection(conn.getRealConnection(), this);
state.idleConnections.add(newConn);
// 复用原连接的时间信息
newConn.setCreatedTimestamp(conn.getCreatedTimestamp());
newConn.setLastUsedTimestamp(conn.getLastUsedTimestamp());
// 将原连接置为无效状态
conn.invalidate();
// 唤醒等待连接的线程
state.notifyAll();
} else {
// 空闲连接集合已满
state.accumulatedCheckoutTime += conn.getCheckoutTime();
// 回滚未提交的事务
if (!conn.getRealConnection().getAutoCommit()) {
conn.getRealConnection().rollback();
}
// 直接将数据库连接关闭
conn.getRealConnection().close();
conn.invalidate();
}
} else {
state.badConnectionCount++;
}
}
}
pushConnection()逻辑比较简单,主要做了两件事情:
- 将连接从活跃连接列表移除
- 如果空闲列表已满,则直接将此连接关闭;如果空闲列表未满,则新建
PooledConnection并复用Connection对象(所以并没有新的TCP握手挥手的开销),并将此连接放入空闲列表。
到此,PooledDataSource的获取连接与释放连接的操作,在连接池中形成了一个闭环。
总结
本文分析了MyBatis内置的连接池的实现方式。当调用方拿连接时,首先会从池中获取。当调用方关闭连接时,MyBatis使用了代理模式拦截此方法,将该连接放回到池中。